Unlocking the Potential of Organic Gardening Modules: A Sustainable Approach to Cultivating Green Spaces
Organic gardening has become increasingly popular as people seek healthier and more sustainable ways to cultivate their food.
With the rise of interest in organic practices, informational sessions on organic gardening modules have become invaluable resources for both novice and experienced gardeners alike.
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-2985789920568613" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Introduction to Organic Gardening Modules
Organic gardening refers to the practice of growing plants without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Instead, organic gardeners rely on natural methods to nourish and protect their plants, promoting soil health and biodiversity in the process.
Benefits of Organic Gardening
Organic gardening offers numerous benefits, ranging from environmental conservation to personal health improvements.
By avoiding harmful chemicals, organic gardeners contribute to soil fertility, water conservation, and wildlife preservation. Additionally, consuming organically grown produce reduces exposure to toxins and promotes a more nutritious diet.
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-2985789920568613" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Understanding Organic Gardening Modules
Organic gardening modules encompass a variety of components, including soil management, plant selection, and pest control. Each aspect plays a crucial role in creating a balanced and sustainable garden ecosystem.
Soil health, in particular, forms the foundation of organic gardening, requiring attention to nutrient levels, pH balance, and microbial activity.
Choosing the Right Organic Gardening Module
Selecting the appropriate organic gardening module depends on factors such as available space, climate conditions, and personal preferences.
Urban dwellers may opt for container gardens or vertical gardening systems, while rural residents might embrace traditional raised beds or permaculture designs. Assessing these variables ensures a harmonious fit between the garden and its surroundings.
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-2985789920568613" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Setting Up an Organic Gardening Module
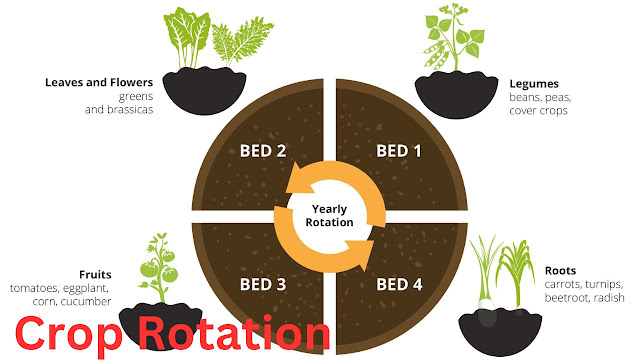
Preparing the soil is the first step in establishing an organic garden, incorporating compost, organic matter, and beneficial microbes to enhance fertility and structure. Plant selection should prioritize native species and heirloom varieties suited to the local climate, with attention to companion planting and crop rotation to minimize pests and diseases.
Regular maintenance, including watering, mulching, and pruning, sustains plant health and productivity throughout the growing season.
Common Challenges in Organic Gardening Modules
Despite their benefits, organic gardening modules may encounter obstacles such as pest infestations, weed competition, and soil imbalances. Integrated pest management (IPM) techniques offer effective solutions, combining biological, cultural, and mechanical interventions to control pests while preserving beneficial insects and wildlife.
Mulching and cover cropping suppress weeds and improve soil structure, while microbial inoculants and organic amendments correct nutrient deficiencies and support plant resilience.
<script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js?client=ca-pub-2985789920568613" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Tips for Successful Organic Gardening Modules
Implementing companion planting strategies, such as intercropping and trap cropping, maximizes space utilization and minimizes pest pressure.
Mulching with organic materials, such as straw or leaves, conserves moisture, regulates soil temperature, and suppresses weeds. Drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting systems minimize water waste and promote deep root growth, reducing the need for supplemental watering.
Community and Support for Organic Gardening
Engaging with local gardening communities provides valuable opportunities for knowledge sharing, seed swapping, and collaborative projects. Online forums and social media groups offer virtual connections to fellow gardeners worldwide, facilitating discussions on organic practices, troubleshooting advice, and inspiration for new projects.
Monitoring and Evaluating Organic Gardening Modules
Regular monitoring of plant health, soil fertility, and pest activity enables proactive management of garden issues before they escalate.
Keeping detailed records of planting dates, yields, and observations facilitates continuous improvement and informed decision-making. Flexibility and adaptability are essential qualities for organic gardeners, who must remain responsive to changing conditions and emerging challenges.
Expanding Organic Gardening Knowledge
Participating in workshops, seminars, and hands-on demonstrations deepens understanding and proficiency in organic gardening techniques. Local agricultural extension offices, botanical gardens, and permaculture institutes offer educational programs tailored to diverse skill levels and interests.
Online courses and webinars provide accessible learning opportunities for aspiring organic gardeners, covering topics such as soil biology, composting, and seed saving.
Case Studies of Successful Organic Gardening Modules
Examples of successful organic gardening modules abound, showcasing innovative approaches to sustainability and productivity. From rooftop gardens in urban jungles to community-supported agriculture (CSA) cooperatives in rural landscapes, these case studies illustrate the transformative power of organic gardening in diverse contexts.
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Future Trends in Organic Gardening Modules
As technology continues to evolve, organic gardening modules will incorporate smart sensors, automated irrigation systems, and data analytics to optimize resource usage and enhance productivity.
Emphasis on regenerative practices, such as no-till farming and carbon sequestration, will mitigate climate change impacts and promote ecological resilience. Collaboration between scientists, farmers, and policymakers will drive innovation and scalability in organic agriculture, ensuring a thriving future for generations to come.
Conclusion
Informational sessions on organic gardening modules offer invaluable insights and practical guidance for aspiring gardeners seeking to cultivate healthy, sustainable food systems. By embracing organic principles and nurturing biodiverse ecosystems, individuals can play a vital role in promoting environmental stewardship and community resilience.
FAQs:
1. What are the primary benefits of organic gardening?
Organic gardening promotes soil health, biodiversity, and personal wellness by avoiding synthetic chemicals and fostering natural ecosystems.
2. How can I start setting up an organic gardening module?
Begin by assessing your space, resources, and gardening goals, then prepare the soil, select suitable plants, and establish a maintenance routine tailored to your needs.
3. What are some common challenges in organic gardening?
Pest management, weed control, and soil fertility are common challenges in organic gardening, but integrated approaches and sustainable practices offer effective solutions.
4. Where can I find support and resources for organic gardening?
Local gardening clubs, online forums, and educational workshops provide valuable support and resources for organic gardeners seeking guidance and community connections.
5. What are some future trends to look out for in organic gardening?
Emerging trends in organic gardening include technology integration, regenerative practices, and interdisciplinary collaborations aimed at fostering innovation and sustainability.





.jpg)






.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)